Essential for managing security, improving efficiency, and ensuring compliance in HR systems.


A user-friendly interface considers topmost the usability and accessibility of a system or application and designs it to make navigation and interaction with the platform easy for users. An important requirement of improving employee satisfaction and engagement within the framework of HRMS or ESS systems, a user-friendly interface has the following basic requirements, benefits, and best practices.
Modern HRMS and ESS systems currently must allow for the characteristic of being available, customizable user roles. This will help organisations customise permissions and access to meet the unique needs and duties of different users. Below is a preview of customisable user roles, with key features, benefits, and best practices for implementation.
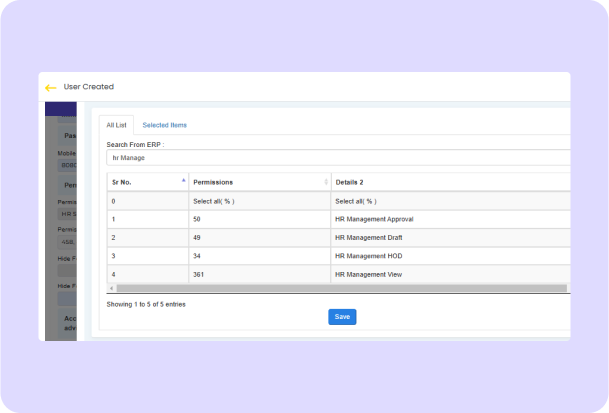
All Employee Self-Service (ESS) or Human Resource Management System (HRMS) must have secure access control. It describes the procedure and equipment used to limit access to features and private data according to user authentication and authorisation. By restricting access to specific pieces of information and actions to authorised personnel only, this serves to protect sensitive organisational and employee data. This is a synopsis of secure access control that covers its main components, benefits, and suggested practices.
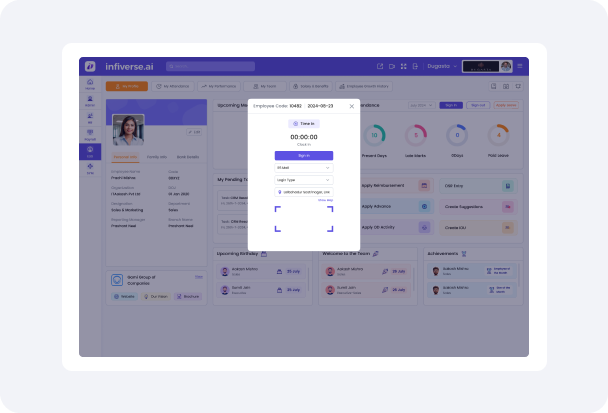

One of the main aspects of modern HRMS and ESS is integration with other systems. To make it exchange data effectively, improve functions, and expedite HR processes, it's necessary to connect the ESS application with several external systems and tools. This is a summary of integration that describes its main elements, benefits, and recommended procedures.
The ability to make minute adjustments to what users can see and do in an organization based on roles, responsibilities, or specific needs is possible through granular permission settings, which allow an organization to further detail specific access controls inside a system. Granular permission settings are critical for HRMS and ESS systems to ensure security, compliance, and user productivity. Here is a more in-depth look at granular permission settings, covering the critical ingredients, advantages, and best practices.
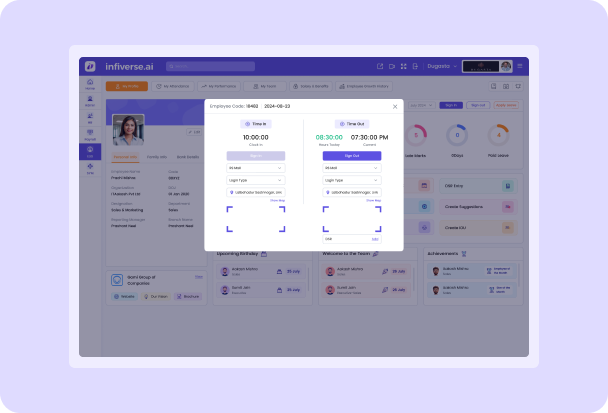
Any good HRMS or ESS should have activity logging and audit trails. They help track user behavior and changes in the system, thus providing security, accountability, and transparency. This is an all-inclusive discussion on the elements, advantages, and best practices of activity logging and audit trails.
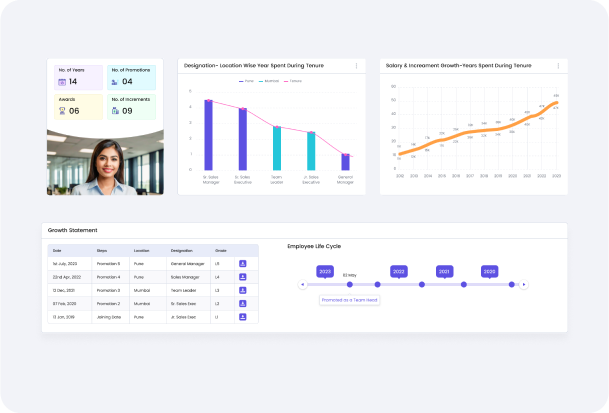
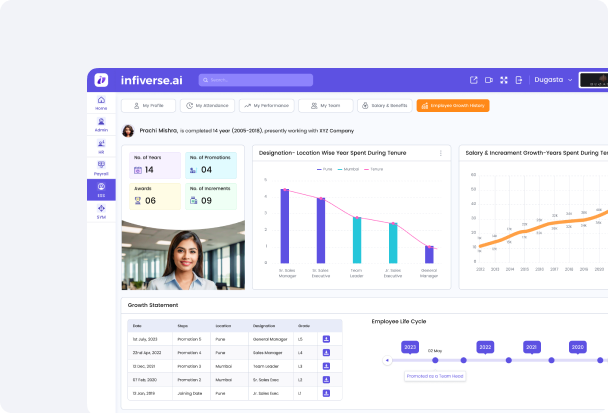
Role-based dashboards are specifically designed user interfaces for improving user efficiency and experience with data and tools centered on a particular user role in an organization. Role-based dashboards enable users to quickly access the information needed and features required by their roles relative to ESS and HRMS. This summary describes role-based dashboards in general terms, including its main characteristics, the advantages and best practices.
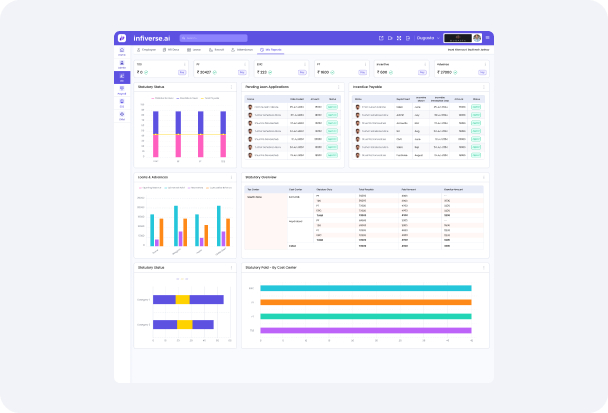

Role-based dashboards are specifically designed user interfaces for improving user efficiency and experience with data and tools centered on a particular user role in an organization. Role-based dashboards enable users to quickly access the information needed and features required by their roles relative to ESS and HRMS. This summary describes role-based dashboards in general terms, including its main characteristics, the advantages and best practices.







Role-Based Accessibility (RBA) is essential for managing security, improving efficiency, and ensuring compliance in HR systems. By restricting access based on roles, you can protect sensitive data, streamline workflows, and create a system that adapts to your organization’s structure. With RBA, you enhance accountability and minimize the risks associated with it.